Squint Surgery
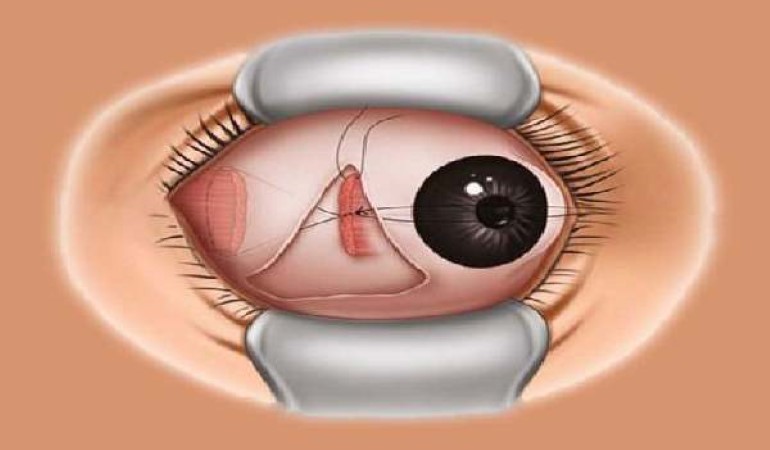
Squint Surgery
Squint surgery, also known as strabismus surgery, is a surgical procedure to correct misaligned eyes. It is a common procedure performed on children, but it can also be performed on adults.
Squint surgery involves adjusting the position of the muscles that control eye movement. This is done by either weakening or strengthening the muscles. The surgeon may choose to operate on one eye or both eyes, depending on the severity of the squint.
Squint surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia, meaning that the patient is asleep during the surgery. The surgery itself typically takes about 30 minutes to complete.
After squint surgery, the patient will need to wear a protective eye patch or shield for a few days. They may also need to use eye drops to prevent infection and inflammation. Most people can return to their normal activities within a week or two of surgery.
Squint surgery can help to improve vision, eye alignment, and depth perception. It can also help to reduce the risk of developing other eye problems, such as amblyopia (lazy eye).
Here are some of the benefits of squint surgery:
• Improved vision
• Improved eye alignment
• Improved depth perception
• Reduced risk of amblyopia (lazy eye)
• Improved appearance
• Increased peripheral vision (side vision)
• Increased self-confidence